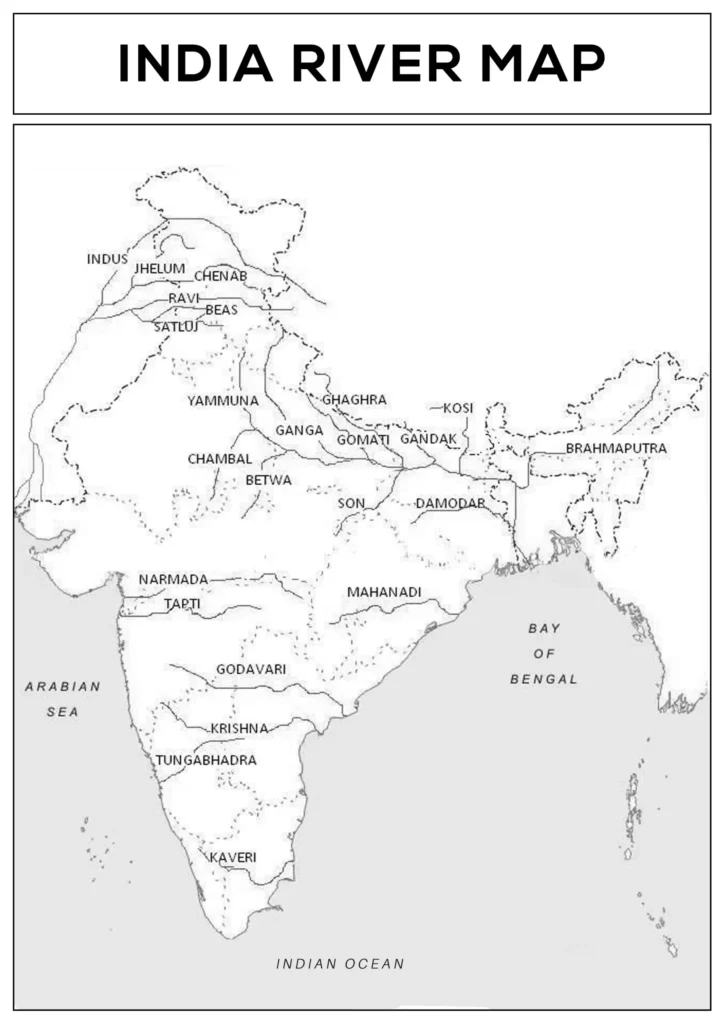
India’s 7 Longest Rivers: A Journey Through the Waterways of the Subcontinent. India, a land of diverse landscapes and rich cultural heritage, is also home to some of the world’s most impressive river systems. These rivers not only provide sustenance to millions of people but also hold immense religious and cultural significance.
images by theprintables.in
1. Indus River: The Lifeline of North India
The Indus River, stretching over 3,180 kilometers, is the longest river in India and the sixth-longest in Asia. Originating in the Tibetan Plateau, the Indus meanders through the rugged terrain of northern India, Pakistan, and finally empties into the Arabian Sea. It is revered as the “cradle of Indian civilization” and has played a pivotal role in the development of agriculture, trade, and culture in the region.
2. Brahmaputra River: A Majestic River of the Eastern Himalayas
The Brahmaputra River, with a length of 2,900 kilometers, is the second-longest river in India and the ninth-longest in the world. It originates in the glaciers of the Himalayas and flows through Tibet, India, and Bangladesh, eventually merging with the Ganges River in Bangladesh. The Brahmaputra is known for its powerful floods, which can cause both devastation and fertile land formation.
3. Ganga River: The Holy River of India
The Ganga River, venerated as the “Ganges” in India, is not only the third-longest river in India but also the most sacred river in Hinduism. With a length of 2,525 kilometers, it originates in the Gangotri Glacier in the Himalayas and traverses through northern and eastern India, eventually draining into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganga is a lifeline for millions of people, providing irrigation, drinking water, and a source of spiritual solace.
4. Godavari River: The Dakshin Ganga, or South Ganges
The Godavari River, also known as the “Dakshin Ganga” or “South Ganges,” is the second-longest river in India south of the Vindhya Mountains. With a length of 1,465 kilometers, it originates in the Brahmagiri Hills of Maharashtra and flows through the Deccan Plateau, eventually merging with the Bay of Bengal. The Godavari River is revered for its religious significance and its contribution to agriculture and irrigation.
5. Krishna River: The Lifeline of South India
The Krishna River, with a length of 1,400 kilometers, is the fourth-longest river in India. Originating in the Western Ghats, it flows through the states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, and Telangana, eventually emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The Krishna River is a vital source of irrigation and drinking water for millions of people, and it also supports a rich biodiversity of aquatic life.
6. Yamuna River: The Tributary of the Ganges
The Yamuna River, with a length of 1,376 kilometers, is the main tributary of the Ganga River. Originating in the Yamunotri Glacier in the Himalayas, it flows through northern India, eventually merging with the Ganga River at Prayagraj. The Yamuna River is a significant source of irrigation and drinking water for the densely populated regions of northern India.
7. Narmada River: The Holy River of Madhya Pradesh
The Narmada River, with a length of 1,312 kilometers, is the fifth-longest river in India. Originating in the Amarkantak Plateau in Madhya Pradesh, it flows westward through the state, eventually emptying into the Gulf of Cambay. The Narmada River is considered a holy river in Hinduism and is home to numerous pilgrimage sites.
These seven rivers, each with its unique character and significance, have shaped the landscape, culture, and history of India. They continue to play a vital role in the lives of millions of people, providing sustenance, spiritual solace, and a connection to the natural world.
10 Longest Rivers in the World: https://wowhana.com/?p=27
1 thought on “7 Longest Rivers of India: Waterways of the Subcontinent.”